某课堂字体逆向以及自动答题
-
起因:一门课老师在某课堂给出了刷题题库,可以无限次提交,直至答对
-
想法:
- 手动做题然后通过导出响应生成题库,考试时直接搜索(选修课,且在手机上考试)
- 自动做题,自动试错,直至答对
-
未来展望
- 实现登录自动获取cookie(目前需要手动提取)
- 实现自动获取所有课程已做过的题目,生成题库
-
该文章中所有代码均已提交至 Github
-
已答题的题库提取
-
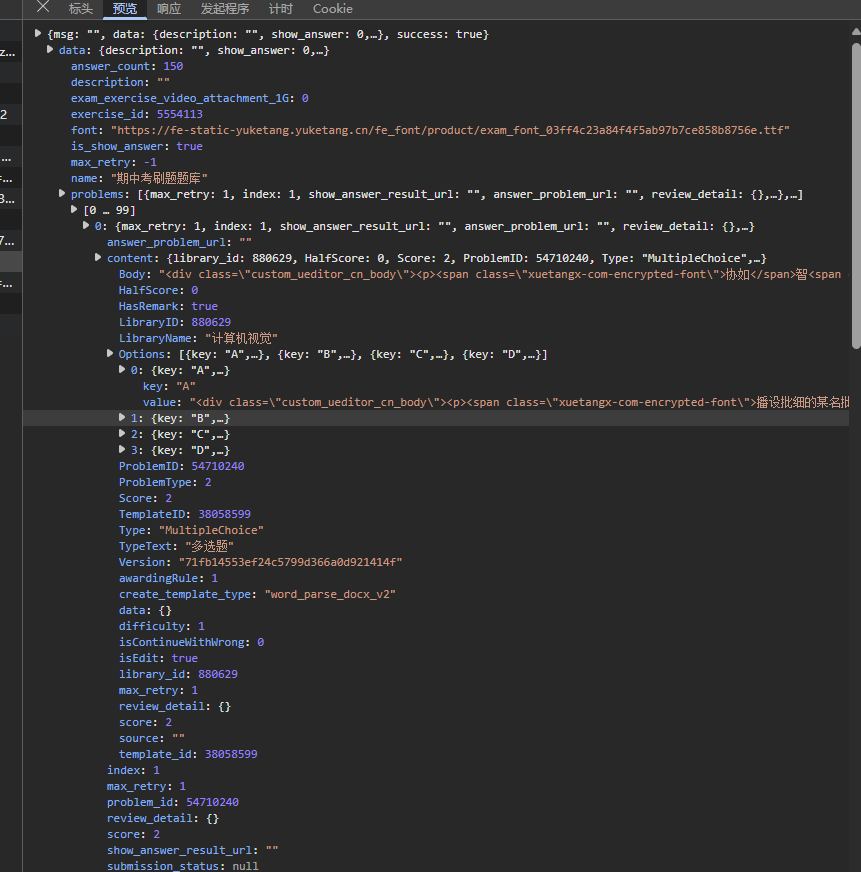
手动保存响应,观察响应格式(类似该格式的请求 https://www.yuketang.cn/mooc-api/v1/lms/exercise/get_exercise_list/5554113/)
-
Body为题目,Options为选项,当答题后可用user下的is_right判断当前答案是否为正确答案
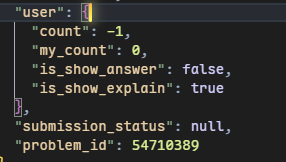
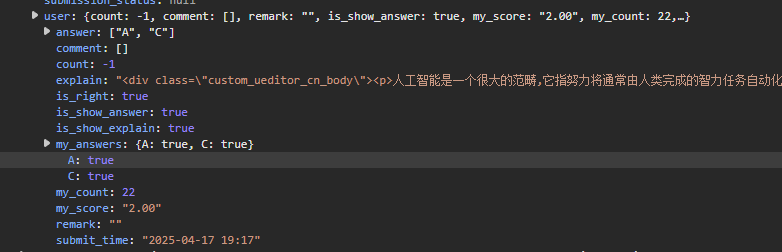
-
本文主题雨课堂字体逆向,参考文章【小记】探探学习平台的字体混淆 - SomeBottle - 博客园
-
核心思想相同字体的字形相同
-
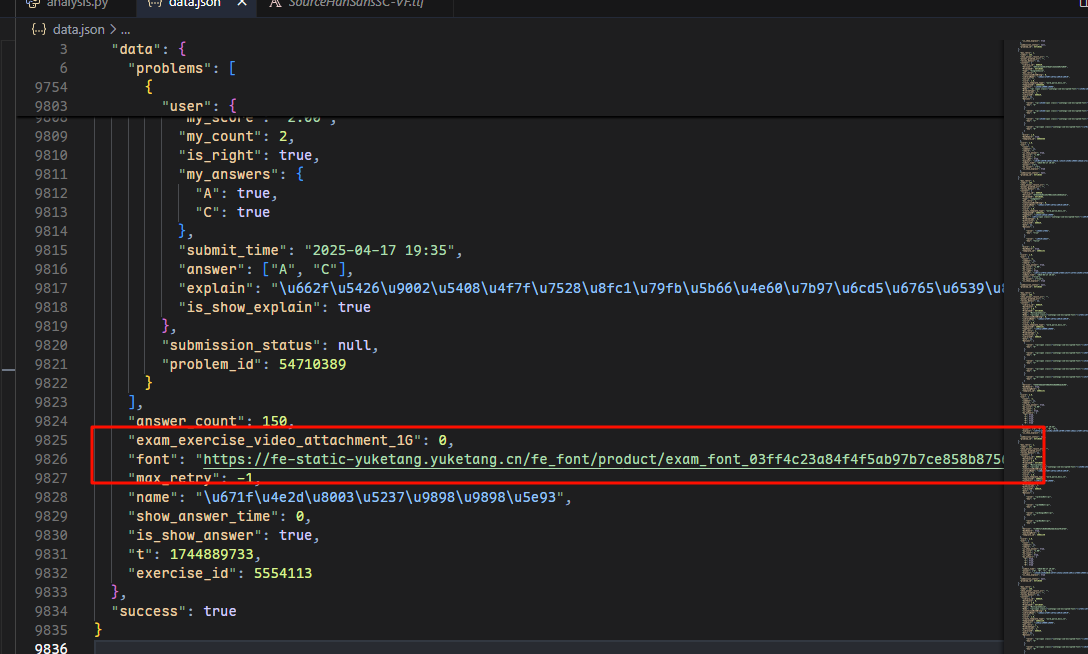
首先从请求中获取加密后的字体(原文章从网页中正则匹配加密字体url)
-
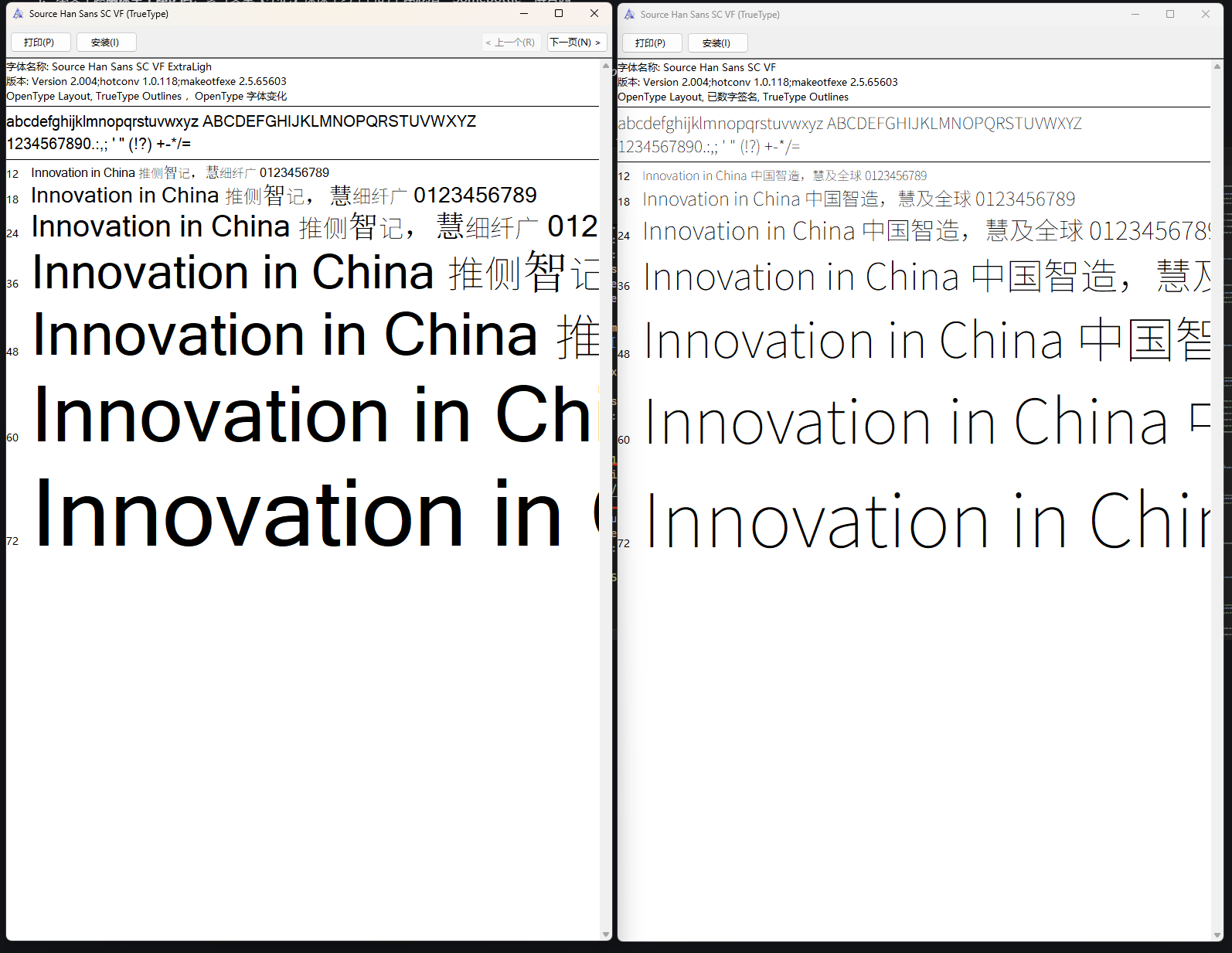
双击打开查看字体信息(左边为加密字体,右边为原字体),从此处也可以看出,只对中文进行了混淆,英文和数字无变化,原字体可从GitHub下载(adobe-fonts/source-han-sans: Source Han Sans | 思源黑体 | 思源黑體 | 思源黑體 香港 | 源ノ角ゴシック | 본고딕)
-
首先由生成原字体和加密字体的字形哈希到Unicode的映射
def extract_glyph_mapping(font_path: str) -> Dict[str, int]:"""从字体文件中提取字形哈希到Unicode的映射参数:font_path: 字体文件路径返回:字形哈希到Unicode的映射字典"""# 加载字体font = load_font(font_path)# 获取字形映射glyphs_to_uni = {}cmap = font.getBestCmap()for unicode_val, glyph_name in cmap.items():glyph = font.getGlyphSet().get(glyph_name)if glyph and hasattr(glyph, 'draw'):# 使用一个自定义路径对象来捕获绘制命令path_collector = PathCollector()glyph.draw(path_collector)glyph_hash = hash_glyph(path_collector.commands)# 如果哈希已存在则跳过 (处理碰撞)if glyph_hash not in glyphs_to_uni:glyphs_to_uni[glyph_hash] = unicode_valreturn glyphs_to_uniclass PathCollector:def __init__(self):self.commands = []def moveTo(self, p):self.commands.append(('moveTo', p[0], p[1]))def lineTo(self, p):self.commands.append(('lineTo', p[0], p[1]))def curveTo(self, *points):self.commands.append(('curveTo', *[(p[0], p[1]) for p in points]))def qCurveTo(self, *points):self.commands.append(('qCurveTo', *[(p[0], p[1]) for p in points]))def closePath(self):self.commands.append(('closePath',)) -
生成完毕后,将两者hash进行比对,若相同,则将加密字体hash所对应的unicode码与正确unicode码建立映射
def create_unicode_mapping(original_mapping_path: str, encrypted_mapping_path: str, output_path: str = './unicode_mapping.json') -> Dict:"""创建加密Unicode到正确Unicode的映射表参数:original_mapping_path: 原始字体字形到Unicode的映射文件路径encrypted_mapping_path: 加密字体字形到Unicode的映射文件路径output_path: 输出映射表的文件路径返回:加密Unicode到正确Unicode的映射字典"""try:# 加载原始映射和加密映射with open(original_mapping_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:original_mapping = json.load(f)with open(encrypted_mapping_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:encrypted_mapping = json.load(f)# 创建反向映射(字形哈希 -> 原始Unicode)hash_to_original_unicode = original_mapping# 创建反向映射(字形哈希 -> 加密Unicode)hash_to_encrypted_unicode = encrypted_mapping# 创建加密Unicode到原始Unicode的映射unicode_mapping = {}# 对于每个字形哈希,找到对应的加密Unicode和原始Unicodefor glyph_hash in hash_to_original_unicode:if glyph_hash in hash_to_encrypted_unicode:encrypted_unicode = hash_to_encrypted_unicode[glyph_hash]original_unicode = hash_to_original_unicode[glyph_hash]# 将加密Unicode映射到原始Unicodeunicode_mapping[str(encrypted_unicode)] = original_unicode# 写入JSON文件with open(output_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:json.dump(unicode_mapping, f,ensure_ascii=False,indent=2)print(f"成功创建Unicode映射表,共 {len(unicode_mapping)} 个映射")return unicode_mappingexcept Exception as e:print(f"创建Unicode映射表失败: {e}")return {} -
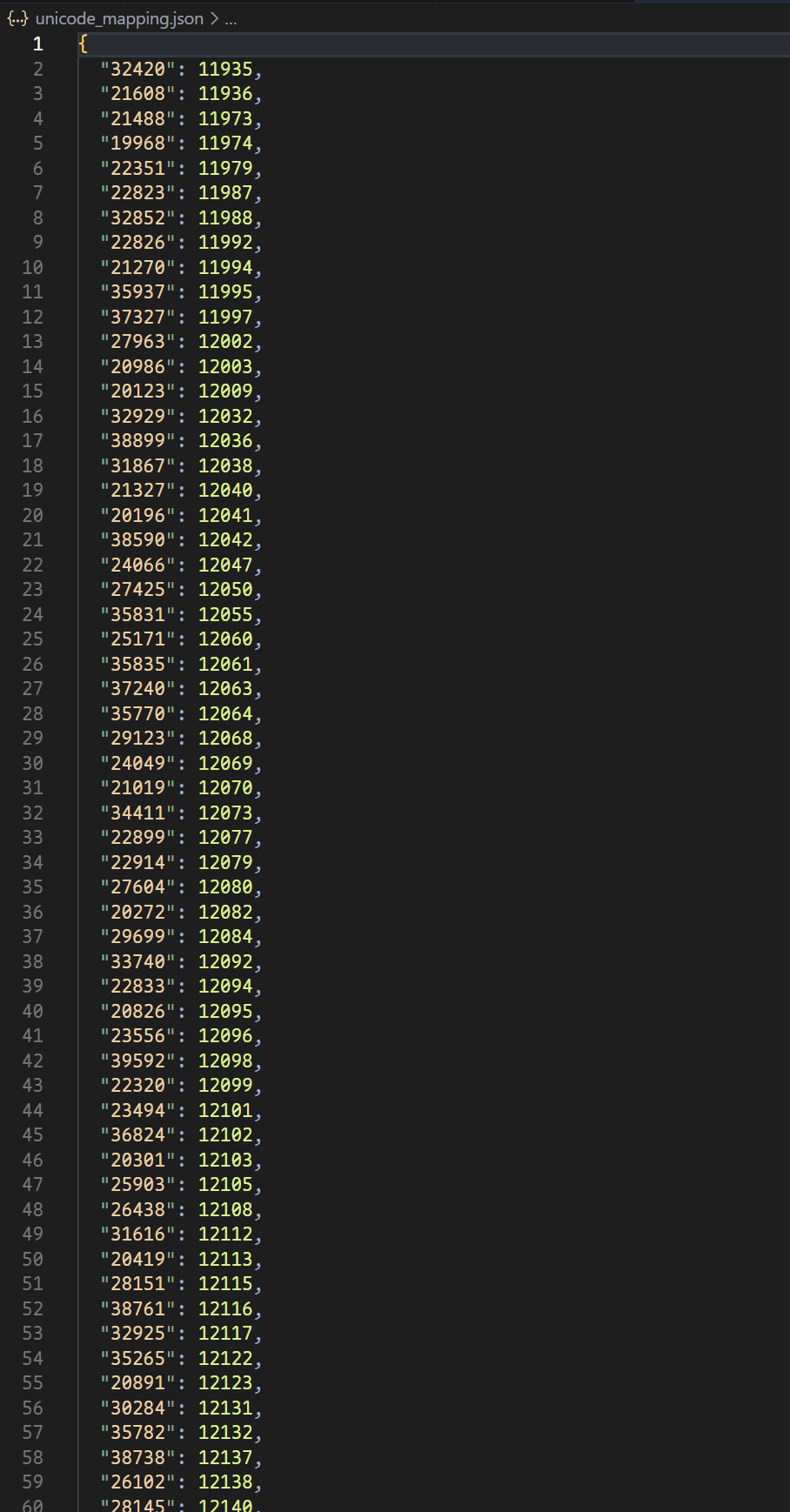
生成正确映射如图(只适用于当前请求,每次请求所使用的加密字体均会变化),此时只需要读取此次请求中加密字体的Unicode码,将其修改为对应Unicode码,则可获取正确的语句
-
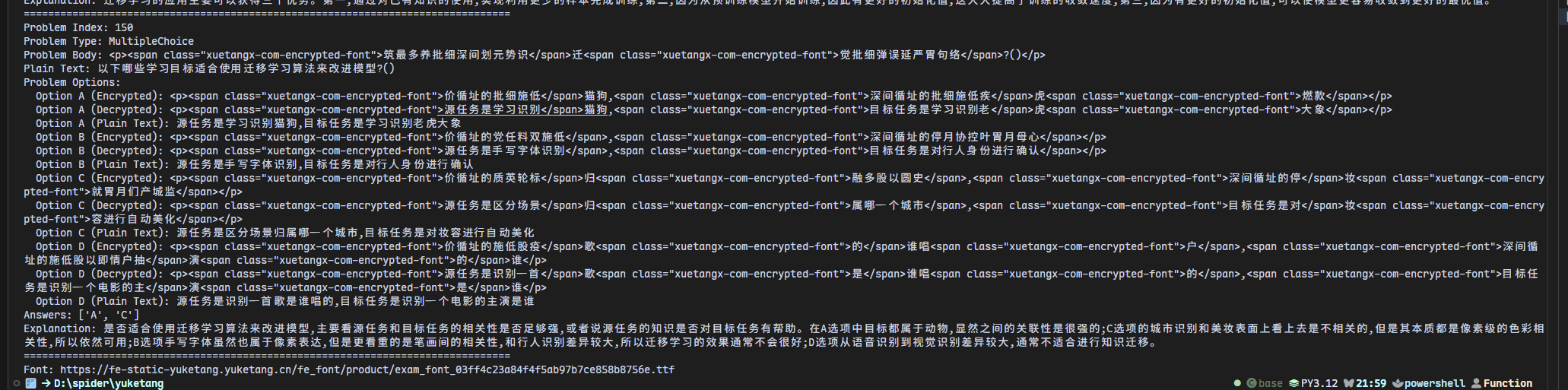
最终结果
-
-
-
自动答题实现
-
建议先通过先前的请求,获取题目的类型以及选项
with open('data.json', 'r') as file:data = json.load(file)# print(data)data = data['data']font_url = data['font']problems = data['problems']# 从第80个题开始处理# problems = problems[80:]for problem in problems:index = problem.get('index', None)content = problem.get('content', None)ProblemID = content.get('ProblemID', None)Type = content.get('Type', None)# 获取所有可用选项Options = content.get('Options', None)options_keys = []if Options:print("Problem Options:")for option in Options:key = option.get('key', '')options_keys.append(key)print(f"\n处理题目 {index}, ID: {ProblemID}, 类型: {Type}")print(f"可用选项: {options_keys}") -
拼接请求体
# 请求体范例json_data = {"classroom_id": 25012730,"problem_id": 54710288,"answer": ["A", "B"],} -
请求体由显而易见的三个字段组成,其中answer有些许需要特殊处理的步骤,若题目类型(Type字段)为单选题或判断题,依次尝试,直至 is_correct 字段返回 True 则为正确答案,若为多选题,则需要提交上面生成的整个答案数组,答案中会返回 my_answer 内部会标出你所提交答案的正确与否,在下次提交中就可以生成正确的答案进行提交
found_answer = Falseif Type == 'SingleChoice':# 依次尝试每个选项for option_key in options_keys:answer = [option_key]print(f"尝试答案: {answer}")json_data = {"classroom_id": 25012730,"problem_id": ProblemID,"answer": answer,}response = make_request_with_rate_limit(post_url, json_data, headers)if response.status_code == 200:response_json = response.json()print(response_json)print(response_json['data'])if response_json['data']['is_correct']:print(f"✓ 找到正确答案: {answer}")found_answer = Truebreakelse:print(f"✗ 答案错误: {answer}")time.sleep(1) # 等待1秒再尝试下一个选项else:print(f"请求失败,状态码: {response.status_code}")if not found_answer:print(f"警告:未能找到题目 {index} (ID: {ProblemID}) 的正确答案")elif Type == 'MultipleChoice':# 提交整个选项列表answer = options_keysprint(f"尝试答案: {answer}")json_data = {"classroom_id": 25012730,"problem_id": ProblemID,"answer": answer,}response = make_request_with_rate_limit(post_url, json_data, headers)if response.status_code == 200:response_json = response.json()print(response_json)my_answers = response_json['data']['my_answers']# 提取正确答案correct_answers = [key for key, value in my_answers.items() if value]# 提取错误答案wrong_answers = [key for key, value in my_answers.items() if not value]# 重新提交正确答案json_data = {"classroom_id": 25012730,"problem_id": ProblemID,"answer": correct_answers,}response = make_request_with_rate_limit(post_url, json_data, headers)print(f"状态码: {response.status_code}")response_json = response.json()if response_json['data']['is_correct']:print(f"✓ 找到正确答案: {correct_answers}")found_answer = Trueelse:print(f"✗ 答案错误: {correct_answers}")elif Type == 'Judgement':# 依次尝试每个选项for option_key in options_keys:answer = [option_key]print(f"尝试答案: {answer}")json_data = {"classroom_id": 25012730,"problem_id": ProblemID,"answer": answer,}response = make_request_with_rate_limit(post_url, json_data, headers)if response.status_code == 200:response_json = response.json()print(response_json)print(response_json['data'])if response_json['data']['is_correct']:print(f"✓ 找到正确答案: {answer}")found_answer = Truebreakelse:print(f"✗ 答案错误: {answer}")else:print(f"请求失败,状态码: {response.status_code}")if not found_answer:print(f"警告:未能找到题目 {index} (ID: {ProblemID}) 的正确答案") -
关于
make_request_with_rate_limit函数的解释,提交过快会触发风控,返回响应代码为429,响应体中含有等待时间,可以通过正则表达式提取,进行等待重试def make_request_with_rate_limit(url, json_data, headers, max_retries=3):"""处理请求,自动处理速率限制并重试"""for retry in range(max_retries):response = requests.post(url, json=json_data, headers=headers)print(f"状态码: {response.status_code}")if response.status_code != 429:return response# 处理 429 错误detail = response.json().get('detail', '')print(f"速率限制: {detail}")wait_time = 5 # 默认等待5秒# 尝试从错误消息中提取等待时间match = re.search(r'Expected available in (\d+\.?\d*) seconds', detail)if match:wait_time = float(match.group(1)) + 2 # 加2秒作为缓冲print(f"等待 {wait_time:.1f} 秒后重试... (尝试 {retry+1}/{max_retries})")# 实现倒计时显示total_seconds = int(wait_time)for remaining in range(total_seconds, 0, -1):sys.stdout.write(f"\r剩余等待时间: {remaining} 秒...")sys.stdout.flush()time.sleep(1)# 清除倒计时行并显示继续执行的信息sys.stdout.write("\r等待完成,正在重试请求... \n")sys.stdout.flush()# 如果所有重试都失败,返回最后一次响应return response
-
